6.2.1 Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs)
The course-level pattern Engineer/Inventor (Engineering Design + Self-directed Learning) provides the intended learning outcomes, disciplinary practice, and pedagogical approach for you.
However, you still need to customise the pattern or add new ILOs to complete your course design.
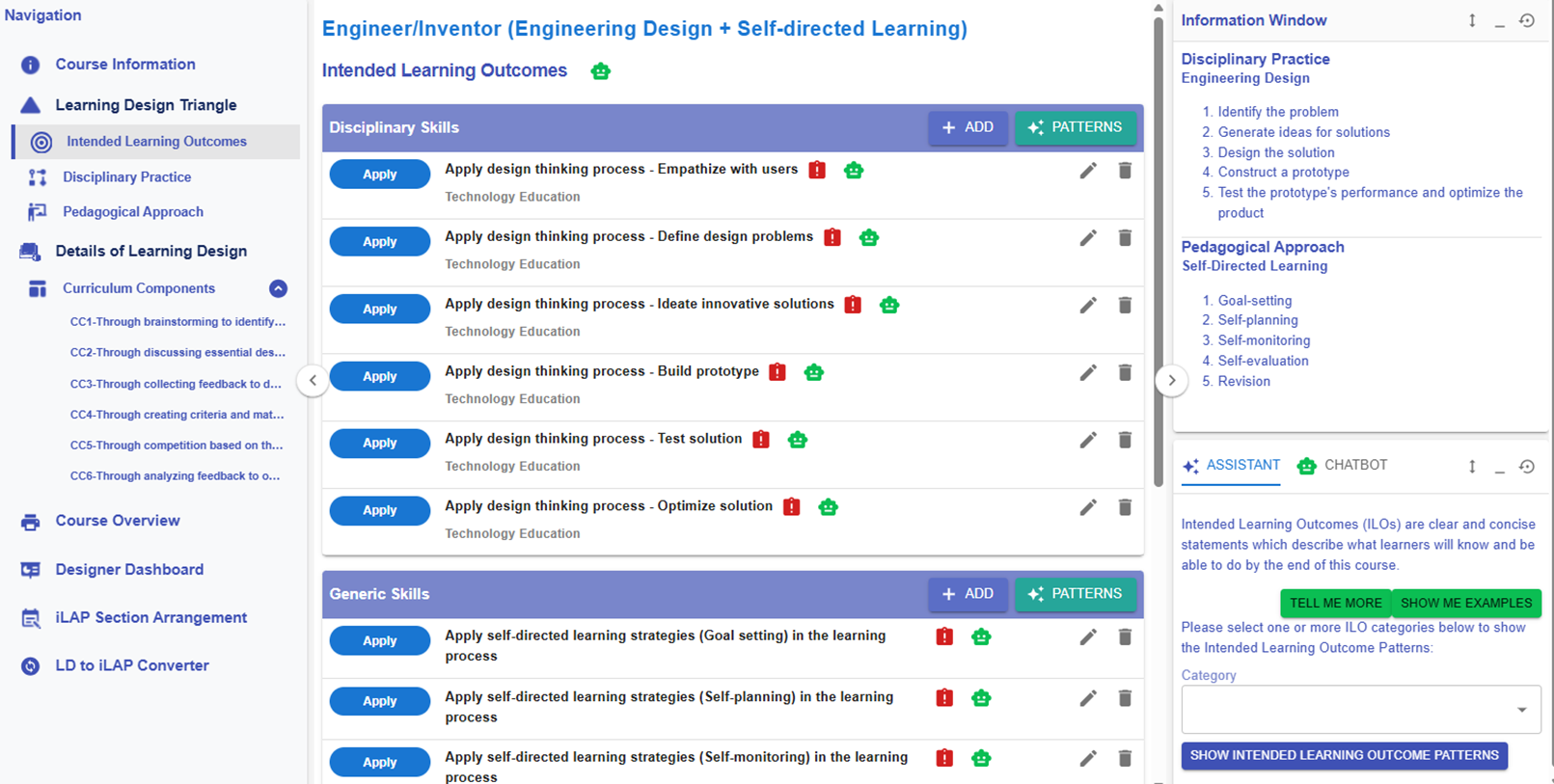
Figure 6.4: Learning Design Triangle Section - Intended Learning Outcomes
For the following part, you will explore how to add the new ILOs to the design.
🌟 For guidance on developing strong ILOs, refer to Chapter 2.2 - Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs)
In the LDS, there are four categories of Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs):
- Disciplinary Knowledge: The core concepts, theories, facts, and frameworks that are recognized and developed within a particular field or area of study.
- Disciplinary Skills: The specific techniques, methods, and competencies associated with a particular field or area of study.
- Generic Skills: The broad abilities that help people succeed in education, work, and daily life, regardless of a particular field or area of study.
- Values & Attitudes: The beliefs, principles, and dispositions that guide a person's behavior, decision-making, and interactions with others.
Adding a New ILO
There are two ways to add a new ILO: (1) using the ILO patterns or (2) writing it yourself.
1. Use the ILO Patterns
- You will use our pre-defined pattern to indicate what students is expected to achieve as a result of the learning process.
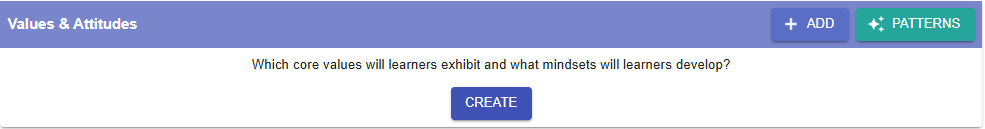
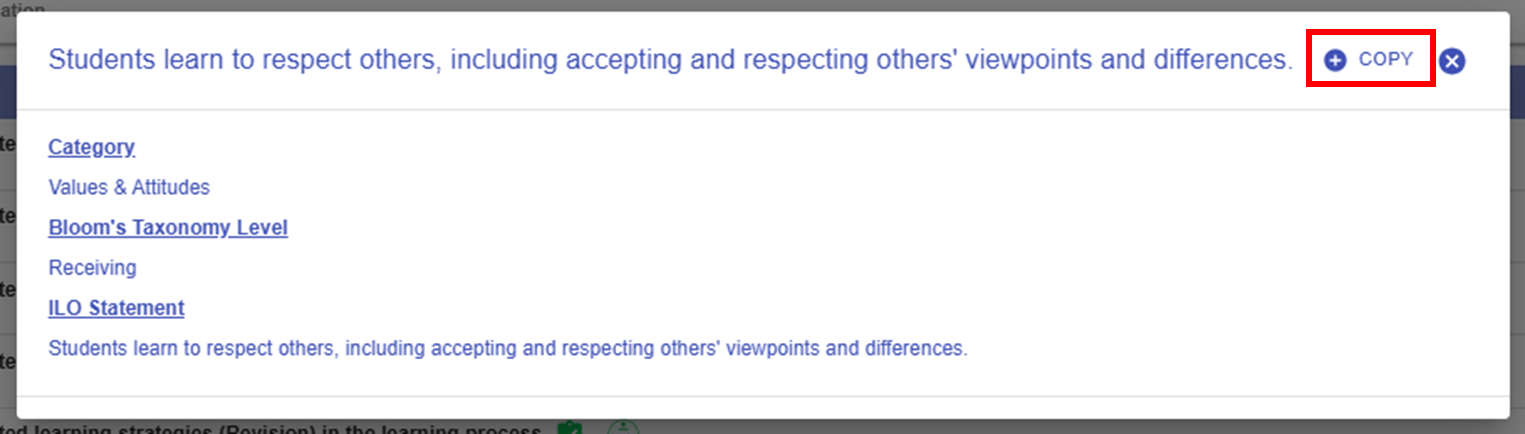
Figure 6.5: Intended Learning Outcomes - Values & Attitude
- For example, if you want to create an ILO for the Values & Attitude category, we can create one by using the ILO patterns.
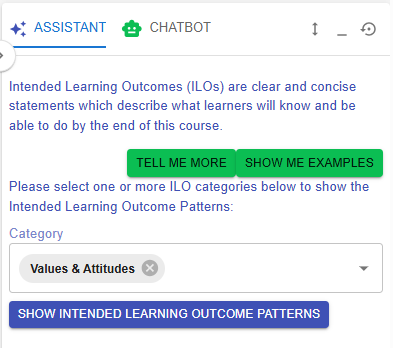 |
 |
|
Figure 6.6: The ILOs Patterns in the LDS Facilitator
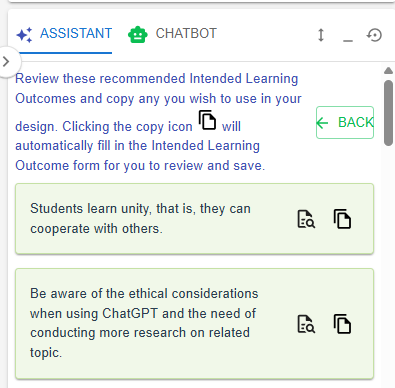
Figure 6.7: Details of the Targeted ILO Pattern (1)
|
|
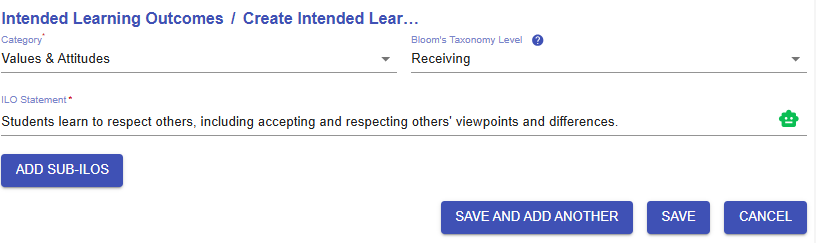
2. Writing it Yourself
YouInwilladdition to using patterns, you may write a full ILOtoyourselfindicate what students are expected to achieve as a result of the learning process..
Figure 6.9: Adding a New ILO
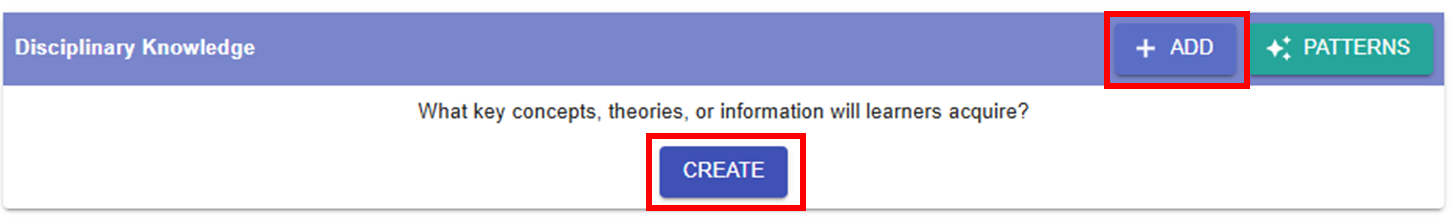
- If you have not added any ILOs before, you can click the
 or
or  button to add a new ILO.
button to add a new ILO.
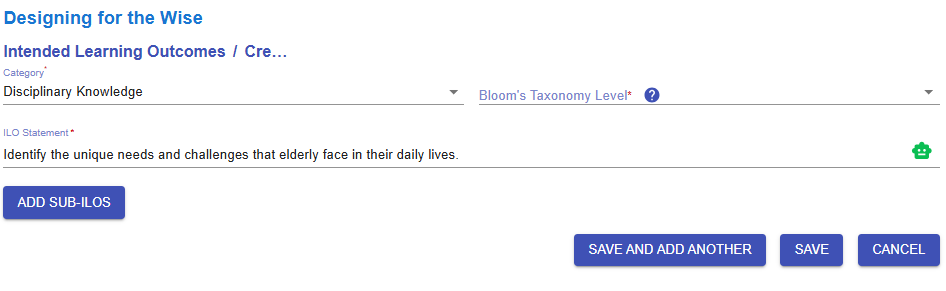
Figure 6.10: Interface of the ILO Builder (1)
- We will review each field in the ILO Builder below.
|
1. Subject/Discipline(s)
Figure 6.11: Interface of the ILO Builder (2)
|
|
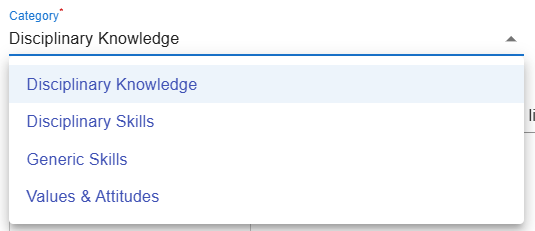
2. Category
Figure 6.12: Interface of the ILO Builder (3)
|
|
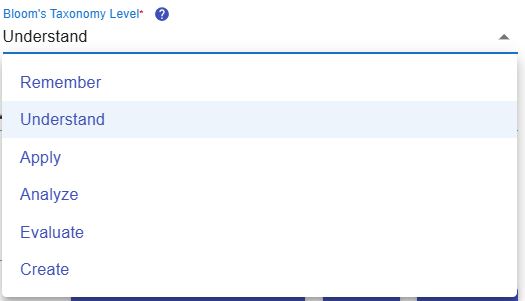
3. Bloom's Taxonomy Level
Figure 6.13: Interface of the ILO Builder (4)
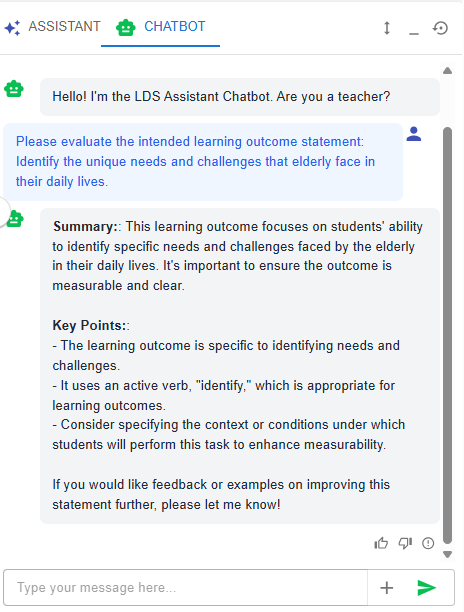
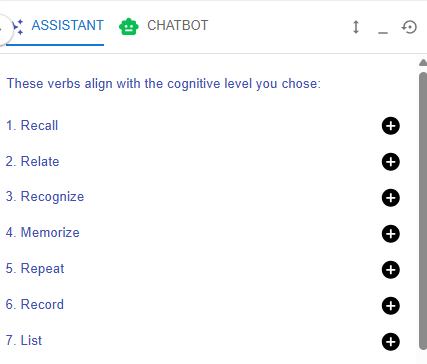 Figure 6.14: Writing a ILO with
|
|
4. ILO and
Figure 6.15: Interface of the ILO Builder (5)
Figure 6.16: Writing a ILO with the Chatbot
|
|
5. Sub-ILO(s)
Figure 6.17: Interface of the ILO Builder (6)
|
After completing this section, it is clear that the ILOs are well defined across Disciplinary Knowledge, Disciplinary Skills, Generic Skills, and Values & Attitudes. The intended cognitive and affective knowledge and skills will guide you in designing appropriate learning experiences later on.

 button to instantly activate the pattern list.
button to instantly activate the pattern list.