2.5.1 Curriculum Component (CC) Example - STEAM Subject
In this section, we will explore how to transform the elements of the Learning Design Triangle to develop a Curriculum Component for a STEAM subject.
Exploring a Sample Learning Design of a STEAM Subject
1. The Learning Design Triangle
Considering that we are designing a curriculum titled "Scientific Investigations in Photosynthesis" and have completed the Learning Design Triangle.
| Linked Intended Learning Outcomes |
[Disciplinary Knowledge]
[Disciplinary Skills]
[General Skills]
[Values and Attitudes]
|
| Workflow Steps of Disciplinary Practice |
Scientific Investigation
|
| Pedagogical Foci |
Self-directed Learning
|
2. The Curriculum Component
The below example will show how to use the information above to create a CC on formulating an inquiry question for goal setting
| CC Name |
A CC name is formed by combining four components.
E.g. Through conducting an interview and searching information online to identify the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis to formulate an inquiry questions for goal-setting
|
|||||||||||||||
| Linked Intended Learning Outcomes |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Workflow Step of Disciplinary Practice | Scientific Investigation-Formulate an inquiry question | |||||||||||||||
| Pedagogical Focus | Self-directed Learning - Goal-setting | |||||||||||||||
| Learning Tasks |
|
3. The Task Sequence in a CC
- A task can be both an activity and an assessment.
- A well-formulated task sequence helps build knowledge and skills step-by-step while enabling ongoing assessment of student understanding.
-
Learning outcomes are easier to manage and assess.
-
The introduction of the task types will be covered in Chapter 2.6 - Task Taxonomy.
4. The CC Sequence
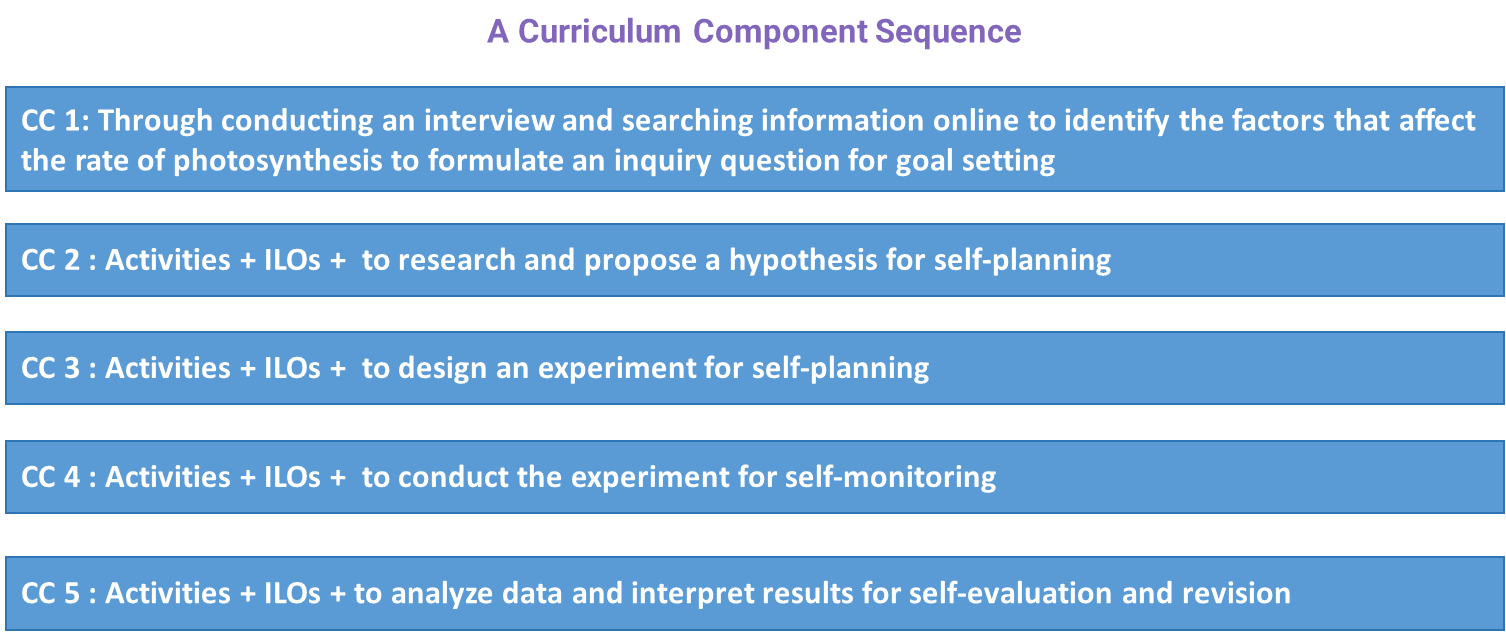
Figure: 2.6 A Curriculum Component Sequence
In order to comprehensively assess all ILOs in the learning design and ensure students experience every step of the disciplinary practice of scientific investigation, the learning design will incorporate additional Curriculum Components (CCs) in a logical order and then forming a CC Sequence.
5. Benefits of Creating a CC Sequence
-
The learning process is organized into multiple stages based on workflow steps and pedagogical foci.
- It ensures every stage has clear intended learning outcomes, targeted activities, and aligned assessments.
- Implementing an outcome-based design approach creates a robust learning experience focused on achieving outcomes rather than being limited by class time.
- It provides the flexibility that supports and enhances self-directed learning.
At the end, the LDS enables you to assign tasks within each CC to create a tailored lesson plan. It bridges your ideal sequence with real classroom needs and constraints, allowing you to revise and adapt the lesson plan for feasibility and effectiveness.

